
SEO, or search engine optimization, is the technique of increasing unpaid or organic traffic to a website by enhancing the visibility of webpages or the entire website in SERPs (search engine results pages). To attain top rankings for your desired keywords, you must use SEO to boost your rank.
While there are several internet tools for improving your SEO practices and using SEO on-page and off-page methods, it is important to avoid typical SEO blunders. Here are some of the most common SEO blunders, as well as solutions for them.
Let’s start by looking at some of the most typical SEO blunders, or difficulties, and how to address them.
Common SEO Mistakes:
1. Slow website speed.
Slow site performance might dissuade visitors from accessing material on your page. Inevitably, sluggish site performance will cost you valuable SEO visitors. If the website takes too long to load, all of your time and work put in driving visitors from SERPs will be for nothing.
To assess your page speed, consider the following performance metrics:
Page Load Time
This is the time it takes between the browser sending the request to the server and your page entirely loading and rendering. Page load time may be analysed using the following factors:
First Contentful Paint.
FCP is a measure monitored in the performance portion of a Google Chrome Lighthouse report. It measures how long it takes (in seconds) for your browser to produce the first piece of DOM (Document Object Model) content once a user navigates to your website.
Here is an example of the FCP’s time series.
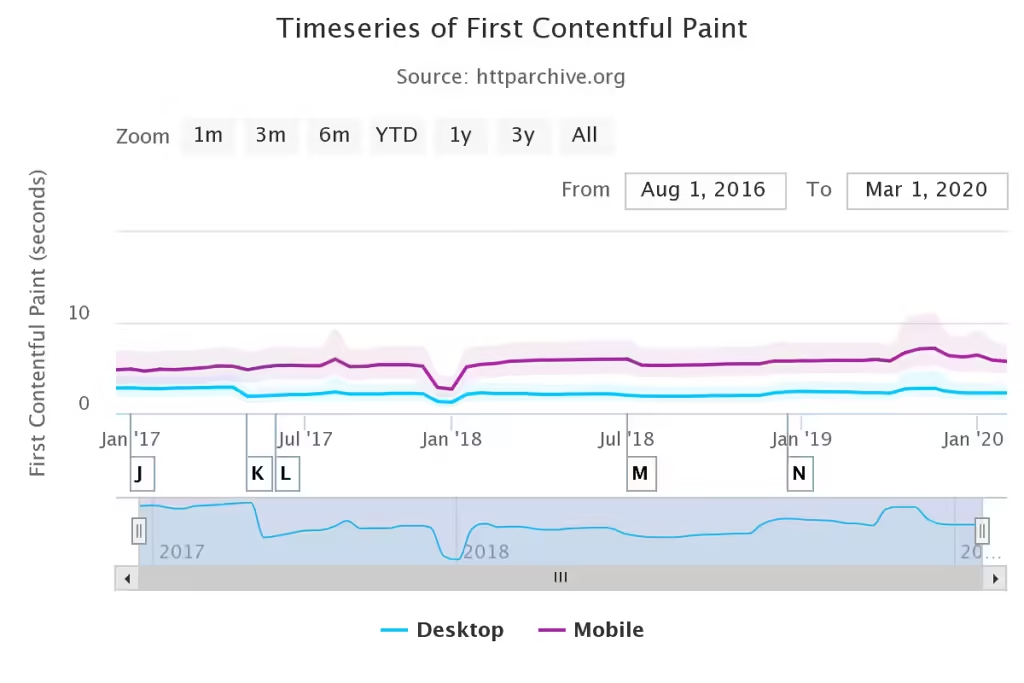
Source: http://archive.org.
It’s time to get interactive
Time to Interactive (TTI) is a statistic that measures page loading speed. In other words, TTI is the time required for the page to become fully interactive. The TTI score is calculated using data from the HTTP archive.
This is an example of a TTI time series.
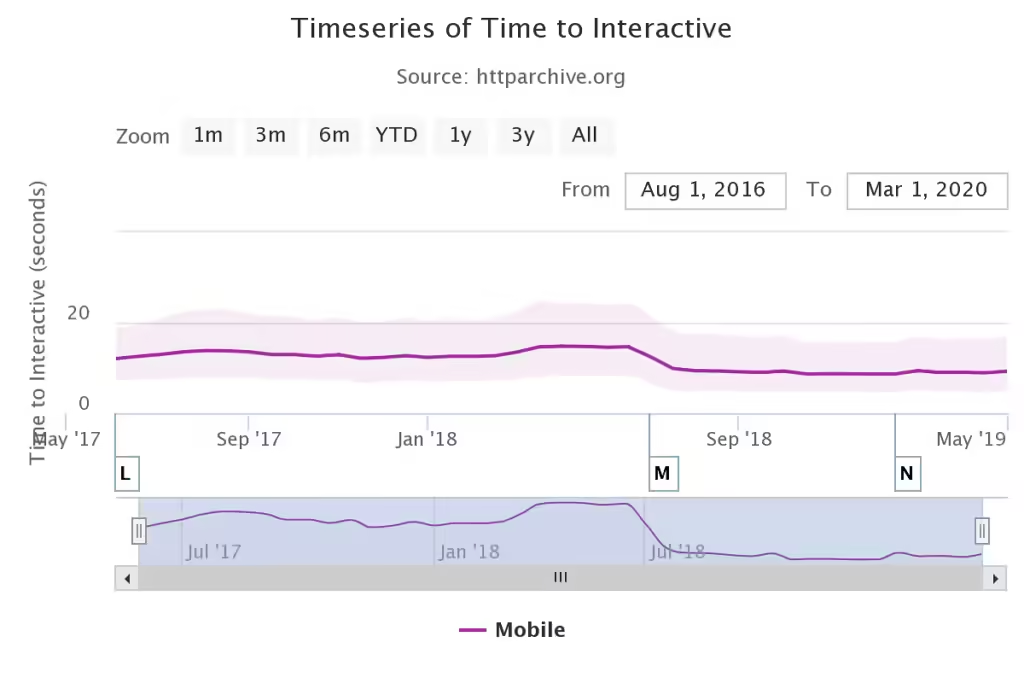
Source: http://archive.org.
Time To First Byte (TTFB)
The time it takes for the browser to receive the first byte of data after sending a request to the server.
Possible fixes
Run your webpage via Google PageSpeed Insights to evaluate its performance and gain a better understanding of your site’s speed. Several causes can cause a delay in page load time, including:
- Image Size and Format: To reduce the bandwidth consumed by photos, set the image size to 72dpi using picture editing tools and image formats such as JPEG 2000, JPEG XR, and WebP.
- Redirects: While certain redirects are inevitable, resolving them will improve server performance. Conduct a site audit of all internal URLs that are creating redirects and fix them.
- Javascript and CSS: Compress JavaScript and CSS code by utilizing shorter variable names to minimize size and, as a result, boost loading time.
2. Bad Google Reviews
When it comes to product or service reviews, one should expect both positive and negative feedback. However, the overall quantity of reviews improves your business’s social proof and helps to localized search ranking considerations. While favourable evaluations increase the legitimacy of your website, having solely positive reviews makes it appear suspicious. At the same time, multiple clients expressing discontent with your website may drive away traffic.
Possible Fix
You may make use of bad reviews as a strategy to create relationships with your customers—helping you understand your audience and, in turn, attract a new audience. Posting on social media about the sorts of challenges experienced and the tactics utilized to handle them can add to your website’s reputation.
Also, with the aid of industry-specific review sites and social media, you may encourage individuals to publish evaluations about your services, and publicly answer their queries to make you look authentic.
3. Faulty Google My Business Verification Code
Encountering issues with the verification PIN you receive for your Google My Business account is a pretty common problem.
Possible Fix
Change your “private” profile to “public” and try again. If this doesn’t work, request a new PIN. The problem may arise after you update your NAP (Name, Address, and Phone Number) details. To avoid this, make sure that your contact information is consistent with your listing.
The next SEO mistake is often made by webmasters, not targeting location-specific pages for their content.
4. Lack of location-specific pages
According to a Google report, searches for location-specific terms including “near me” have increased, particularly among mobile users. Between 2013 and 2017, mobile searches for “..near me” increased by 900 percent. Furthermore, 76 percent of consumers who use their mobile device to look for something nearby go to the linked company within a day or so, and 28 percent of those searches end in a purchase.
As the number of mobile consumers has grown, many businesses have realized that local presence is vital. High-quality, location-specific, or regionally optimized content is a crucial component of both global and local SEO strategies.
Possible Fix
Recognizing your brand with a local presence should enhance your rating in the local search results considerably more accessible. The possible answer for this SEO blunder is to create well-optimized location-specific unique pages to assist enhance your ranking in local SERPs. Clear location signals are natural when you have a single place.
The next SEO error is having duplicate content on your site.
5. Duplicate material.
Duplicate content refers to content that is similar or identical to other content on your website. Although Google does not punish duplicate content, it is quite likely to degrade webpage rankings. Because search engines seldom display identical copies of two pieces of information in SERPs, they select the one that appears most relevant to consumers.
Possible Fix
Because content is king on any website, having unique material that provides the audience with credible information about your products or services will help you establish yourself as a trustworthy market player. To avoid this SEO issue, make sure that any material you post on your website is not copied elsewhere. For example, you may utilise Copyscape to detect and delete duplicate material from your website.
The second SEO concern is failing to address broken pictures in a timely way.
6. Graphics are broken, and alternative text is missing.
Alternative tags, often known as alt tags, are HTML characteristics that assist explain an image’s content. Alt tags must be updated to solve on-page SEO issues. The picture component on your website may not display correctly owing to an improper filename, file location, or extension. In some circumstances, the image’s alt tag will describe its content and purpose on the page. It also reinforces the chosen keyword by assisting crawlers in understanding the page’s content. Broken photographs and missing alt tags are regular issues.
Figure: A broken picture with alt tags.
Possible Fix
It is simple to use alt tags. Add an alt tag to the photo component in your HTML code. Here’s an illustration of an image source.
If you have a WordPress blog, you can easily post these photographs.
Let us now explore another typical SEO issue with content: having obsolete or irrelevant material on the page.
7. Outdated content and information on the webpage.
Old content on your website may diminish its authority. The SERP returns a large number of search results for a given query, but not all of them are relevant to readers. If the search engine determines that your content is out of date or irrelevant, your website will be removed. You will waste your site’s crawl quota by crawling and indexing sites that are no longer relevant. It may cost you visitors to your website because the bounce rate on such pages will increase.
Possible Fix
To avoid this SEO blunder, ensure that the content you upload is high-quality and relevant. Always offer search engines high-quality, well-optimized content.
Learn More about: Website Performance Optimization
The second most common SEO issue is a website that is not mobile friendly.
8. You do not optimise your website for mobile devices.
In today’s mobile-first world, many people rely on mobile devices instead of computers. There are several benefits to having mobile-friendly websites, which account for more than half of Google’s search results. Simultaneously, if your page is not mobile-friendly, you may lose visitors. If you have not used this feature, your website is missing out on some of the most advanced design options.
Perficient Digital’s survey reveals the percentage of site visits received from mobile vs. desktop between 2016 and 2018.
Source: Perficient Digital.
Possible Fix
Having a mobile-friendly website helps you rank higher in SERPs. A mobile-optimized website is by far the most complex type of design. Because it is mobile optimised, the site will automatically reformat for different devices. When you optimise your website for mobile, you increase both its performance and design structure.
You may use the Mobile-Friendly Test tool to see if your page is mobile-friendly. If you discover that your site is not mobile-friendly, select a reputable web host, optimise your site’s loading speed, activate Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP), and adapt your pop-ups for mobile devices.
The next SEO error that we often overlook is having contact forms that do not convert.
9. Contact Form isn’t converting.
According to Formisimo, just 49% of the 1.5 million visitors who see a form fill it out. Furthermore, just 16% of the viewers complete it. There are various reasons why contact forms do not lead to conversions, including:
Too many form fields.
The submit button is unclear or does not operate.
Too few or too many selections in the dropdowns.
Possible Fix
Make your contact form engaging and straightforward to fill out. Also, to remedy this SEO issue, supply fewer form fields to increase conversions.
- Make your contact form minimal, with no more than five essential fields.
- Concentrate on the form alignment.
- Create a distinctive, one-of-a-kind call to action.
- Conduct A/B testing on your form’s design characteristics, such as colour, position, size, essential fields, and so on.
- The Google autocomplete plugin allows you to enable auto-fill for your form.
- Ensure that your form is optimised for mobile.
- Do not use CAPTCHA.
The second most common SEO error is having faulty landing pages.
10. Broken linkages.
When consumers access your site via a search engine and see a 404 error, it produces a terrible image. Broken links on your website may even diminish your crawl budget, which affects how many times Google crawlers will crawl your page in a specific timeframe. When search bots locate multiple broken links, they will proceed to other websites, leaving some of your key pages unindexed or crawled. It also has a severe influence on your page’s domain authority.
Possible Fix
Using Google Search Console‘s crawl stats tool, you may detect which pages on your site are returning a 404 error.
You may even use Ahrefs to detect broken links. The following strategy can help you find broken links using Ahrefs.
Site Explorer -> yourdomain.com -> Pages -> Best Links -> Add a “404 not found” HTTP response filter.
To improve your SEO, repair any broken web pages as quickly as feasible. To fix the broken links:
- Replace or rebuild the page’s content.
- Use 301 redirects to send your visitors to a similar piece of information on your website.
- Contact the webmaster for a fast resolution to any external links. If the domain is no longer working, you may simply delete it or replace it with a new source.
11. A Low Ratio of Text to HTML
Due of its closer relationship to technical SEO, this SEO faux pas will also receive less attention. Behind the written content of your webpage comes the HTML code, which includes headers, links, JavaScript, graphics, and more. From what the search engine finds on the same page, text-to-HTML compares the ratio of text content to that of HTML code.
The optimal text-to-HTML ratio, according to woorank, is between 25% and 70%. Google also utilizes this statistic to verify the relevancy of a web page, thus if your text to HTML ratio is low, it means there are serious issues with your website’s on-page technical SEO.
Low ratios could indicate:
- Slow-loading websites, as a result of excessive code
- Hidden text—a red flag for search bots
- Excessive use if Flash, inline styling, and JavaScript
Possible Fix
An indication to enhance website load speeds is a low text to HTML ratio. An HTML rich webpage can negatively impact loading times and user experience. To rectify this SEO faux pas, include pertinent on-page content whenever required, extract superfluous code, and relocate inline scripts to their own files. If you want your webpage to be as little as possible, utilize simply text on-page.
One of the most often made SEO mistake is not checking if you’re pages are getting indexed by Google or not.
12. Indexed Pages
When your webpages are indexable, Google adds them to its collection of searchable pages. Anything that Google’s bots don’t crawl can’t be ranked. There can be a number of legitimate reasons why search engines are ignoring your pages:
- 404 Not found pages
- Every time your sites have meta tags that contain the code cannot be included in search results
- You need to update your sitemap.
- Same material twice
- Not very well-known or influential
Fix Potential
Google Search Console is the gold standard for fixing indexing problems. You may check if a website’s URL is indexed when you submit an inspection request.
You may mimic the way search engine bots scan your site with the aid of Deepcrawl, a complete website crawler. If you want a thorough report for each URL, you may dive deep without slowing down your site.
Enabling robots.txt for certain websites. Wait for Google to recrawl your pages once you’ve done this.
If you want to crawl your website using Screaming Frog, change the user-agent to “Googlebot,” “Bingbot,” “Slurp,” “DuckDuckBot,” “Baiduspider,” or “YandexBot.” Verify that any page that is not now indexed may be indexed by looking at the “Indexability” column.
Make sure your XML sitemaps aren’t packed with broken or misdirected links.
Indexing Content on Web Pages
13. Meta description and title tag length is incorrect.
One element in HTML that determines a web page’s title is the meta title, sometimes known as the title tag. As a brief overview of your page’s content, the meta description element is an essential SEO component. A specific search engine results page (SERP) will display them.
Meta Title
The ideal structure for a meta title is as follows: Primary Keyword | secondary keyword | Brand Name.
Depending on the character width (Google shows titles that are roughly 600 pixels), the ideal length of the meta title is 50-60 characters.
Not only do meta titles appear on search engine results pages (SERPs), but they also appear in the browser and on social media.
Meta Description
Between 50 and 160 characters is the sweet spot for a meta description. Even while meta descriptions don’t have an effect on SEO in and of themselves, they do influence CTR and, consequently, ranks. Meta descriptions may have an indirect effect on search engine optimization.
The following issues can develop while working with meta description:
- Meta description tags that are duplicated
- Overly wordy meta descriptions cause targeted keywords to disappear.
- Meta descriptions that use numeric numbers (possible solution)
Make sure your meta description has obvious calls to action included. Make use of your chosen keywords and keep the meta description and title tags within the recommended length to prevent Google from cutting off your keywords.
Meta Description
- Use your SEO keywords sparingly in the title tags. If you want to divide up your terms in the title tag, use pipes. Make sure your titles aren’t just a jumble of meaningless terms; they should be easy for people to understand.
- A poor user experience could still result from social sharing services registering the first text they find on your page—regardless of whether you utilize the meta description element or not. In addition, each page’s title tag and meta description should be different.
Long, unfriendly URLs that neither readers nor search engines can easily parse are the second most overlooked SEO faux pas.
14. Clumsy, Prolonged URLs
One way to find a certain web page on the internet is by looking for its Uniform Resource Locator (URL). For optimal performance across all browsers and to prevent Google’s truncation, URLs should not exceed 2083 characters (or 512 pixels) in length.
Improved user experience and increased search exposure are two ways in which URLs may help SEO.
Some of the most common causes of poorly legible URLs, which discourage people from clicking on them, are as follows:
- Making excessive use of fasteners
- Such characters as , %, and # are being included.
- Substituting HTTP for HTTPS
- Topping up your URLs with more than two directories
Possible Fix
Both humans and search engines benefit from carefully constructed URLs, as pointed out by Moz.
See how important it is for URLs to be easy to read in the example below:
Making URLs Easy to Understand
- Your social media links will be more clickable if they have readable URLs.
- A shorter URL is more likely to rank higher than a larger one, which in turn increases the likelihood of direct traffic.
- A secure version of HyperText Transfer Protocol, or HTTPS, is available. The security of a website is greatly enhanced since all data stored on it is encrypted.
- Relevant keywords should be included in URLs.
- In the URL, hyphens, not spaces, should separate keywords.
- It is imperative that all characters in the URL be lowercase.
The second common SEO faux pas is using incorrect redirects, which is something that anyone from a novice to an expert user would do.
15. Mistaken Redirects
Redirects may cause your SEO value and visitors to decrease. It may be time to tidy up your redirects if they aren’t doing any good. Even though they accumulate over time, many 301 redirects no longer provide the SEO benefit they formerly did. Your page’s load time and bounce rate will both rise as a result of this.
Possible Fix
- In case you haven’t already, switch from the HTTP version of your page to the HTTPS version.
- The Screaming Frog can power your website. You may remove all sitemap internal links with 301 redirects using the All Inlinks report, which is accessible from the Bulk Export option.
- Revamp your site by fixing all the faulty redirects.
- Locate and correct every loop and redirect chain
- Redirect 404 pages
In summary
Increasing user engagement and providing high-quality content should be your top SEO priorities at all times. Even if certain SEO blunders could be attributed to human error, maintaining a routine site audit will assist you in keeping your site healthy.
Learn More from Best SEO Agency in India